Equipment
Museum: Museum is well established with adequate weapons and models.
WEAPONS

Semiautomatic rifled firearm
Description of weapon – Shoulder
arm with long rifled barrel, magazine and bolt action.
Injuries produced by weapon – Firearm
wounds, fracture by butt.
Medicolegal aspects – Mostly
used for homicidal.

Pistol
Description of weapon – Hand
arm, small rifled barrel, semiautomatic.
Injuries produced by weapon – Firearm
wounds.
Medicolegal aspects – Homicidal,
suicidal and accidental.
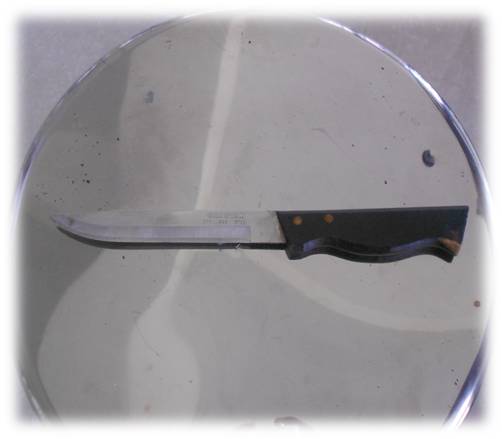

Kitchen knife
Description of weapon – Light
sharp cutting weapon with pointed tip, metal blade with two edges.
One edge is sharp cutting, serrated and other edge is blunt. Handle
is made up of plastic.
Injuries produced by weapon – Incised
wound, stab (punctured, penetrating, perforating) wound.
Medicolegal aspects – homicidal,
suicidal, accidental & Self- inflicted/fabricated wounds.
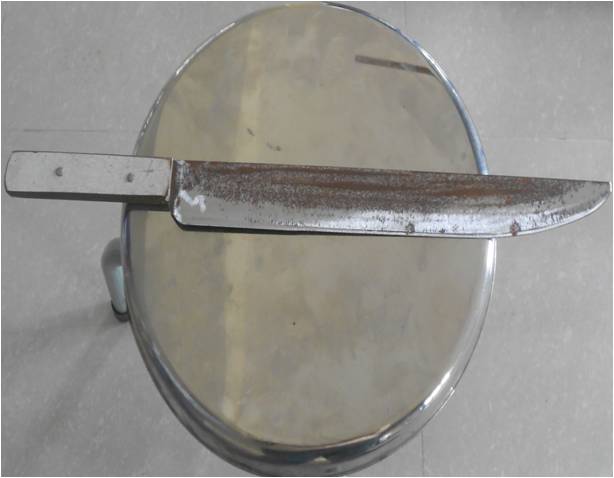

Kitchen knife
Description of weapon – Light
sharp cutting weapon with pointed tip, metal blade with two edges.
One edge is sharp cutting with serrated margins and other edge is
blunt. Handle is made up of wood.
Injuries produced by weapon – Incised
wound, stab (punctured, penetrating, perforating) wound
Medicolegal aspects – Self-
inflicted/fabricated wounds, accidental may cause beveled cuts and
used for homicide and suicide
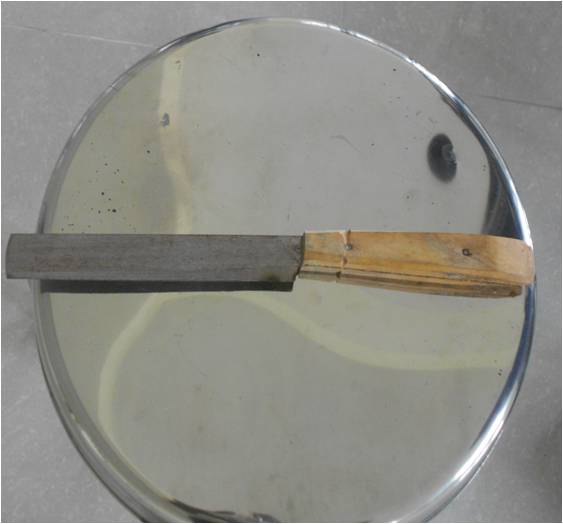

Kitchen knife
Description of weapon – Light sharp
cutting weapon with blunt tip, metal blade with two edges. One edge
is sharp cutting and other edge is blunt. Handle is made up of
wood.
Injuries produced by weapon – Incised
wound.
Medicolegal aspects – Self-
inflicted/fabricated wounds, accidental may cause beveled cuts and
used for homicide and suicide.
 Hunting
Sickle
Hunting
Sickle
Description of weapon – Heavy
sharp cutting weapon, two edges, one edge is sharp and concave.
Other edge is blunt and convex thicker than the sharp edge. Wooden
handle is fitted with the metal part.
Injuries produced by weapon – Chop
wound, cut fractures of the bones, abrasion, contusion and lacerated
wounds by the handle.
Medicolegal aspects – Mostly
used for homicidal purpose.

Hammer
Description of weapon – Heavy
hard blunt weapon, striking surface is circular on one side and
other side is knob like. In between there is hole/loop to
accommodate the handle.
Injuries produced by weapon – Depressed
fracture on the skull.Abrasion, contusion, laceration & fracture
Medicolegal aspects – Mostly
homicidal – ‘Fracture –a-la-signature’.Sometimes accidental.

Wooden Log
Description of weapon – Moderately
heavy hard blunt,made of wood, non flexible weapon, elongated
roller, with smooth surface all around.
Injuries produced by weapon – Lacerated
wound on the skull may resemble incised wound so called
incised-looking wound.
Contusion & abrasions, fracture & dislocations.
Medicolegal aspects – Mostly
homicidal head injuries.
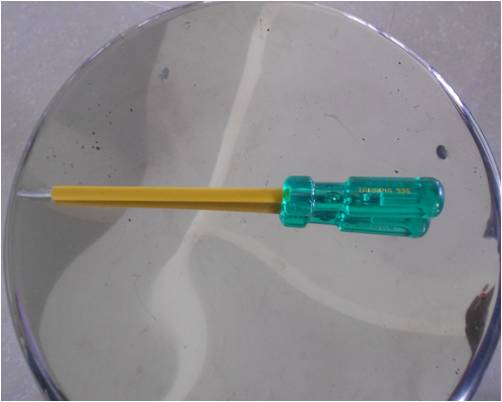 Screwdriver
Screwdriver
Description of weapon – Moderately
heavy blunt weapon, long circular shaped one end with sharp edges
and other end fixed with the handle.
Injuries produced by weapon – Punctured,
perforating, penetrating wound.
Medicolegal aspects – Accidental
and homicidal.
 Motorcycle
chain
Motorcycle
chain
Description of weapon – Made
of iron screws and bolts which are arranged in a regular pattern.
Injuries produced by weapon – Patterned
abrasion, laceration, contusion.
Medicolegal aspects – Homicidal
(strangulation). Used in gang wars & riots.
STONE
Blunt weapon causing
abrasion, contusion and laceration type of mechanical injuries.
 BRICK
BRICK
Blunt weapon causing
abrasion, contusion and laceration type of mechanical injuries.
1. Museum:
Museum is well established with adequate specimens and models.
TOXICOLOGY SPECIMEN

Castor
seeds (RICINUS COMMUNIS)
Identification – Oval
shaped, glossy brown in colour and mottled in appearance, it
resembles croton tiglium in size and shape.
Fatal dose – 10
seeds on average
Fatal period – 36
to 48 hours
Active principles –Ricin.
Mode of Action –Toxic
principle-ricin (toxalbumin), more poisonous than cobra
venom.
Clinical features – Burning
in mouth, throat and stomach, drowsiness, shallow breathing,
dehydration, collapse.
PM findings – Haemorrhagic
inflammation of the GI tract, dilation of heart, haemorrhages in
internal organs.
Medicolegal aspects – Accidental
poisoning in children, powder - conjunctivitis.
 AbrusPrecatorius
AbrusPrecatorius
Identification – Small
egg shaped, bright scarlet coloured with a black dot at one end.
Fatal dose – 90
to 120 mg or 1 to 2 seeds
Fatal period – 3
to 5 days
Active principles –Abrin,
Abrine
Mode of Action –Abrin inhibits
protein synthesis and causes cell death.
Clinical features – Irritation
of upper GI tract, delayed cytotoxic effects on CNS, liver, kidney
and adrenal glands. Resembles viper snake bite.
PM findings – Fragments
of needle found in the skin. Petechial haemorrhage seen on skin,
pleura, pericardium & peritoneum. All internal organs congested.
Medicolegal aspects – Killing
cattle by ‘suis’. Sharp pointed spikes or needles made by paste of
abrusseeds, datura, opium, onion, rectified spirit and water.
Malingerers use powered seeds to produce conjunctivitis.
 Poppy
seeds
Poppy
seeds
Identification – Small
pinhead-sized grayish seeds.
Uses - as
food (nutritious)
Crude opium
Fatal dose – Crude
opium 2 g
Fatal period – 6 to
12 hours
Mode of Action –Opiate
drugs activate receptor sites (endorphins), depresses all centres.
Clinical features –Stage
of excitement, stage of stupor and stage of coma.
PM findings – Signs
of asphyxia is prominent, froth at mouth and nostrils and disappears
rapidly from cadaver.
Medicolegal aspects – Sedative
and narcotic. Intoxication or addiction to incapacitate victim
during commission of some crime.

StrychnosNux Vomica seeds
Identification – Ashy
grey, light hard, flat rounded disc with convexity on one surface
and concavity on the other and appears like the button of a coat.
Fatal dose – 1
to 2 seeds or 30 to 100 mg of strychnine
Fatal period – 1
to 2 hours
Active principle–
Strychnine, Brucine.
Mode of Action –Blocks
ventral horn motor neuron postganglionic receptor sites in the
spinal cord & brainstem and prevent the effect of glycine.
Clinical features –Opisthotonus,
emprosthotonus, pleurosthotonus and risussardonicus.
PM findings – Rigor
mortis appears early, signs of asphyxia. All other organs are
congested.
Medicolegal aspects – Homicide
and suicide are rare because of bitter taste, accidental more common
due to overdose medicinal preparation.

Aconite Root
Identification – Brownish,
conical or tapering in shape, arched and shriveled with longitudinal
ridges.
Fatal dose – 1
to 2 gm of powdered root
Fatal period – 1 to
4 hours
Active principle- Aconitine,
Pseudo-Aconitine, Indaconitine.
Mode of Action –Stimulates
nerve endings causing tingling and later paralysis, effects on
medullary centres and spinal cord.
Clinical features –Burning
sensation mouth to stomach, tingling and numbness all over the body, Hippus.
PM findings – Asphyxial
signs, unstable and is destroyed by putrefaction.
Medicolegal aspects – used
as ideal homicidal poison. Accidental poisoning is due to eating the
roots in mistake for horseradish root. Also used as suicidal,
abortifacient, cattle and arrow poison.
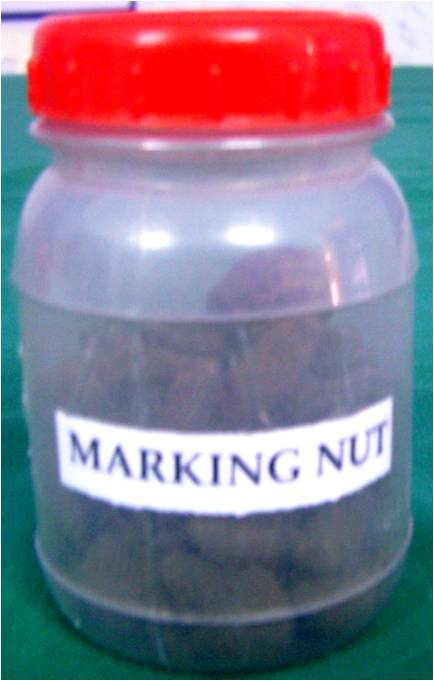 Marking
nut
Marking
nut
Identification – Heart-shaped,
black, hard, with an ashy grey stalk at the base, weighs 1.6 to 3.6
gm.
Fatal dose – 5
to 10 gm on average
Fatal period – 12
to 24 hours
Active principles- Semecarpol
and Bhilawanol.
Clinical features – Acrid
serum produces eczematous lesion, resembles a bruise.
PM findings – Blisters
in mouth &throat , stomach congested & inflamed.
Medicolegal aspects – used
by Washermen to mark on clothing and linens.Homicidal and suicidal
poisoning is rare. Accidental poisoning is by quacks. Juice produces artificial
bruise.
 Cannabis
indica (Ganja)
Cannabis
indica (Ganja)
Identification – Flowering
tops with very little leaves of the female cannabis plant.
Fatal dose – 8
– 10g
Fatal period – Not
known
Active principle – Cannabinol&CannabidiolàTetrahydrocannabinol
Mode of Action –CNS
stimulant.
Forms of abuse - Bhang,
Majoon, Ganja and Charas or Hashish.
Clinical features – Psychiatric
and physical symptoms, chronic poisoning causes Run
amok .
PM findings –signs
of asphyxia.
Medicolegal aspects –Most
widely abused drug in the world. Poisoning occurs due to
overindulgence or accidental ingestion or inhalation. Used by
criminals to strengthen nerves.
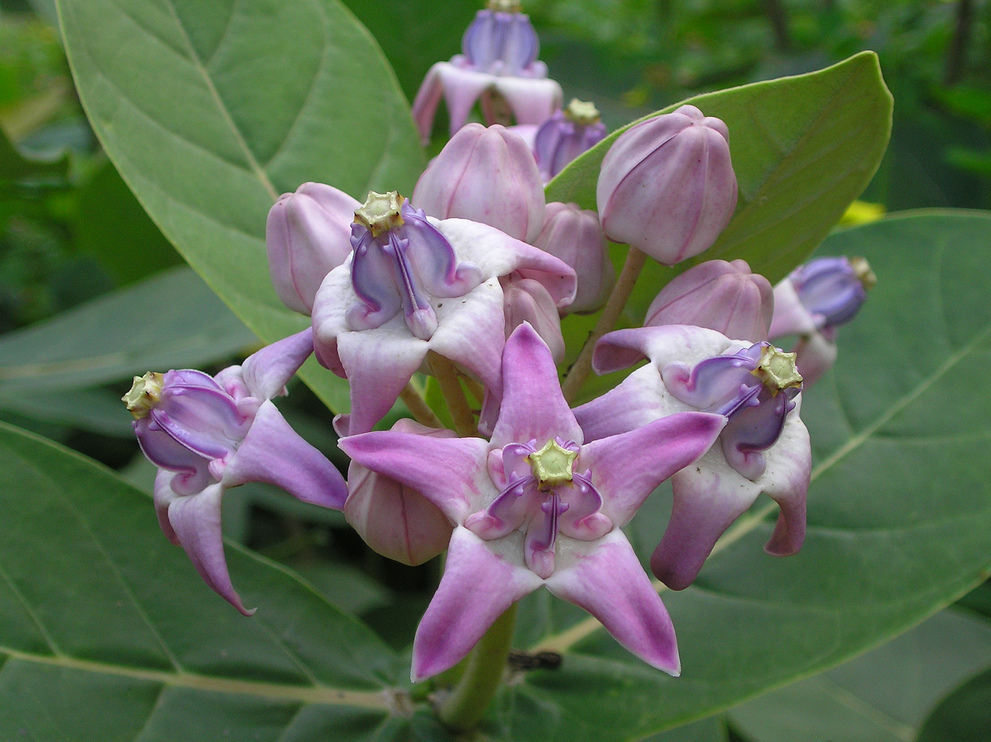 CALOTROPIS
CALOTROPIS
Organic Irritant Poison.Calotropis
gigantic has purple flowers, Calotropisprocera has white flowers.
Ingredients:Uscarin,
Calotoxin and Calotropin. Milky juice- Trypsin.
Fatal Dose: Uncertain.
Fatal Period: 6
to 12 hours.
ML Importance: Indian
Medicine, Twigs and juice for Criminal Abortion, Infanticide, Juice
as vesicant, depilatory, Cattle poisoning, artificial bruise.

CHILLIES (CAPSICUM ANNUM) AND CHILLY SEEDS
Organic Irritant Poison:-
Not poisonous.
Ingredients: Capsaicin
and Capsaicin.
ML Importance: To
facilitate robbery, for confession and torture.
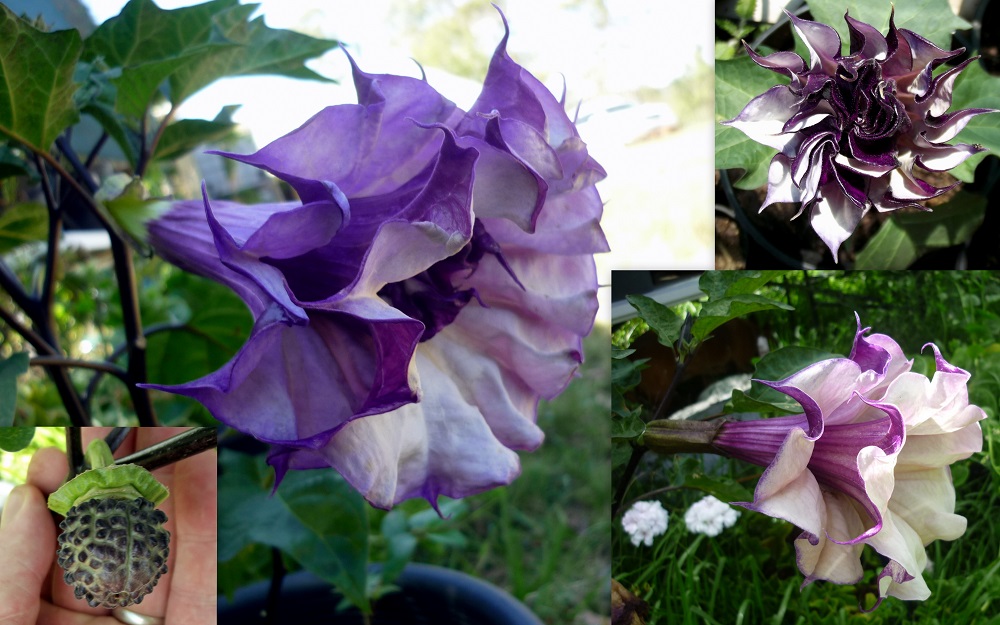 DATURA
FASTUOSA PLANT
DATURA
FASTUOSA PLANT
Deliriant poison.
Ingredients: Atropine,,Hyoscyamine,
Hyoscine and scopolamine.
Fatal Dose: 0.6
To one gram (100 to 125 seeds).
Fatal Period: 24
hours.
Antidote:Physostigmine.
ML Importance: Road
poisoning for robbery, rape or kidnapping by stupefying.
